如何判断一个点是否属于某条线?
如果可能的话,我们会赞赏示例。
在最简单的形式中,只需将坐标插入直线方程并检查是否相等。
鉴于:
Point p (X=4, Y=5)
Line l (Slope=1, YIntersect=1)
插入 X 和 Y:
Y = Slope * X + YIntersect
=> 5 = 1 * 4 + 1
=> 5 = 5
所以,是的,重点就在眼前。
如果您的线以 (X1,Y1),(X2,Y2) 形式表示,那么您可以计算斜率:
Slope = (y1 - y2) / (x1-x2)
然后用这个得到 Y-Intersect:
YIntersect = - Slope * X1 + Y1;
编辑:我修复了 Y 相交(一直是 X1 / Y1 ...)
你必须检查那x1 - x2不是0。如果是,那么检查该点是否在线是一个简单的问题,即检查您的点中的 Y 值是否等于x1或x2。此外,请检查该点的 X 是否不是“x1”或“x2”。
我刚刚编写了一个函数来处理一些额外的要求,因为我在绘图应用程序中使用了这个检查:
private const double SELECTION_FUZZINESS = 3;
internal override bool ContainsPoint(Point point)
{
LineGeometry lineGeo = geometry as LineGeometry;
Point leftPoint;
Point rightPoint;
// Normalize start/end to left right to make the offset calc simpler.
if (lineGeo.StartPoint.X <= lineGeo.EndPoint.X)
{
leftPoint = lineGeo.StartPoint;
rightPoint = lineGeo.EndPoint;
}
else
{
leftPoint = lineGeo.EndPoint;
rightPoint = lineGeo.StartPoint;
}
// If point is out of bounds, no need to do further checks.
if (point.X + SELECTION_FUZZINESS < leftPoint.X || rightPoint.X < point.X - SELECTION_FUZZINESS)
return false;
else if (point.Y + SELECTION_FUZZINESS < Math.Min(leftPoint.Y, rightPoint.Y) || Math.Max(leftPoint.Y, rightPoint.Y) < point.Y - SELECTION_FUZZINESS)
return false;
double deltaX = rightPoint.X - leftPoint.X;
double deltaY = rightPoint.Y - leftPoint.Y;
// If the line is straight, the earlier boundary check is enough to determine that the point is on the line.
// Also prevents division by zero exceptions.
if (deltaX == 0 || deltaY == 0)
return true;
double slope = deltaY / deltaX;
double offset = leftPoint.Y - leftPoint.X * slope;
double calculatedY = point.X * slope + offset;
// Check calculated Y matches the points Y coord with some easing.
bool lineContains = point.Y - SELECTION_FUZZINESS <= calculatedY && calculatedY <= point.Y + SELECTION_FUZZINESS;
return lineContains;
}
确定点 R = (rx, ry) 是否位于连接点 P = (px, py) 和 Q = (qx, qy) 的线上的最佳方法是检查矩阵的行列式是否
{{qx - px, qy - py}, {rx - px, ry - py}},
即 (qx - px) * (ry - py) - (qy - py) * (rx - px) 接近于 0。与发布的其他解决方案相比,此解决方案具有几个相关优势:首先,它不需要垂直线的特殊情况,第二,它不会除法(通常是一个缓慢的操作),第三,当线条几乎但不是完全垂直时,它不会触发不良的浮点行为。
给定线上的两个点L0和L1要测试的点P。
(L1 - L0) * (P - L0)
n = (P - L0) - --------------------- (L1 - L0)
(L1 - L0) * (L1 - L0)
向量的范数n是点P到通过L0和的线的距离L1。如果此距离为零或足够小(在舍入误差的情况下),则该点位于线上。
符号*代表点积。
例子
P = (5, 5)
L0 = (0, 10)
L1 = (20, -10)
L1 - L0 = (20, -20)
P - L0 = (5, -5)
(20, -20) * (5, -5)
n = (5, -5) - --------------------- (20, -20)
(20, -20) * (20, -20)
200
= (5, -5) - --- (20, -20)
800
= (5, -5) - (5, -5)
= (0, 0)
我认为Patrick McDonald 先生给出了几乎正确的答案,这是对他答案的更正:
public bool IsOnLine(Point endPoint1, Point endPoint2, Point checkPoint)
{
return (((double)checkPoint.Y - endPoint1.Y)) / ((double)(checkPoint.X - endPoint1.X))
== ((double)(endPoint2.Y - endPoint1.Y)) / ((double)(endPoint2.X - endPoint1.X));
}
当然还有很多其他的正确答案,尤其是 Mr.Josh,但我发现这是最好的答案。
谢谢大家。
y = m * x + c
这是一条线的方程。x & y 是坐标。每条线的特征在于它的斜率 (m) 以及它与 y 轴 (c) 相交的位置。
因此,给定一条线的 m & c,您可以通过检查等式是否适用于 x = x1 和 y = y1 来确定点 (x1, y1) 是否在线上
二维线通常使用两个变量 x 和 y 的方程来表示,这里是一个众所周知的方程
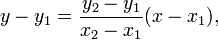
现在想象您的 GDI+ 线是从 (0,0) 到 (100, 100) 绘制的,然后 m=(0-100)/(0-100) = 1 的值因此您的线的等式是 y-0=1 *(x-0) => y=x
既然我们有一个关于这条线的方程,那么很容易测试一个点是否属于这条线。当您替换 x=x3 和 y=y3 时,如果给定点 (x3, y3) 满足直线方程,则它属于该直线。例如,点 (10, 10) 属于这条线,因为 10=10,但 (10,12) 不属于这条线,因为 12 != 10。
注意:对于垂直线,斜率 (m) 的值是无限的,但对于这种特殊情况,您可以直接使用垂直线的方程 x=c,其中 c = x1 = x2。
虽然我不得不说我不确定这是否是最有效的方法。当我手头有更多时间时,我会尝试找到更有效的方法。
希望这可以帮助。
如果您有一条由其端点定义的线
PointF pt1, pt2;
你有一点要检查
PointF checkPoint;
那么你可以定义一个函数如下:
bool IsOnLine(PointF endPoint1, PointF endPoint2, PointF checkPoint)
{
return (checkPoint.Y - endPoint1.Y) / (endPoint2.Y - endPoint1.Y)
== (checkPoint.X - endPoint1.X) / (endPoint2.X - endPoint1.X);
}
并按如下方式调用它:
if (IsOnLine(pt1, pt2, checkPoint) {
// Is on line
}
不过,您将需要检查除以零。
直线方程为:
y = mx + c
所以一个点(a,b)在这条线上,如果它满足这个方程,即b = ma + c
作为该方法的替代slope/y-intercept方法,我使用以下方法选择了这种方法Math.Atan2:
// as an extension method
public static bool Intersects(this Vector2 v, LineSegment s) {
// check from line segment start perspective
var reference = Math.Atan2(s.Start.Y - s.End.Y, s.Start.X - s.End.X);
var aTanTest = Math.Atan2(s.Start.Y - v.Y, s.Start.X - v.X);
// check from line segment end perspective
if (reference == aTanTest) {
reference = Math.Atan2(s.End.Y - s.Start.Y, s.End.X - s.Start.X);
aTanTest = Math.Atan2(s.End.Y - v.Y, s.End.X - v.X);
}
return reference == aTanTest;
}
第一次检查reference确定从线段起点到终点的 arcTan。然后从起点角度,我们确定arcTan到vector v。
如果这些值相等,我们从端点的角度进行检查。
简单并处理水平、垂直和介于两者之间的所有其他内容。