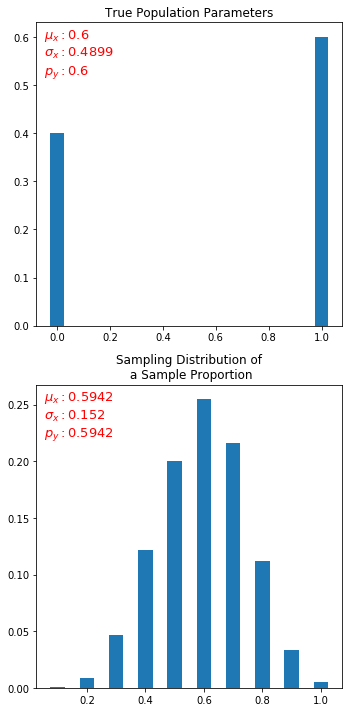
我试图使用 Python 模拟“样本比例的抽样分布”。我尝试使用伯努利变量,如示例here
关键是,在大量的口香糖中,我们有真正比例为0.6的黄色球。如果我们抽取样本(一些大小,比如 10 个),取其平均值并绘图,我们应该得到一个正态分布。
我试图在 python 中做,但我总是得到均匀分布(或在中间平坦)。我无法理解我错过了什么。
程序:
from SDSP import create_bernoulli_population, get_frequency_df
from random import shuffle, choices
from bi_to_nor_demo import get_metrics, bare_minimal_plot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
N = 10000 # 10000 balls
p = 0.6 # probability of yellow ball is 0.6, and others (1-0.6)=>0.4
n_pickups = 1000 # sample size
n_experiments = 100 # I dont know what this is called
# generate population
population = create_bernoulli_population(N,p)
theor_df = get_frequency_df(population)
theor_df
# choose sample, take mean and add to X_mean_list. Do this for n_experiments times
X_hat = []
X_mean_list = []
for each_experiment in range(n_experiments):
X_hat = choices(population, k=n_pickups) # this method is with replacement
shuffle(population)
X_mean = sum(X_hat)/len(X_hat)
X_mean_list.append(X_mean)
# plot X_mean_list as bar graph
stats_df = get_frequency_df(X_mean_list)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(5,5))
X = stats_df['x'].tolist()
P = stats_df['p(x)'].tolist()
ax.bar(X, P, color="C0")
plt.show()
依赖函数:
bi_to_nor_demo
SDSP
更新: 我什至尝试了如下统一分布,但得到了类似的输出。不收敛到正常:(。(使用下面的函数代替 create_bernoulli_population)
def create_uniform_population(N, Y=[]):
"""
Given the total size of population N,
this function generates list of those outcomes uniformly distributed
population list
N - Population size, eg N=10000
p - probability of interested outcome
Returns the outcomes spread out in population as a list
"""
uniform_p = 1/len(Y)
print(uniform_p)
total_pops = []
for i in range(0,len(Y)):
each_o = [i]*(int(uniform_p*N))
total_pops += each_o
shuffle(total_pops)
return total_pops