我正在为 AES-GCM 实现做一个 GHASH。
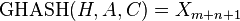
我需要实现这个
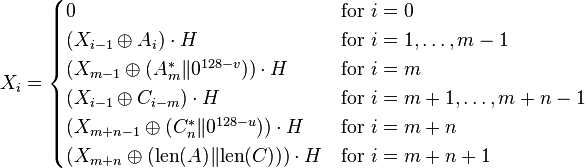
其中v是A的最后一个块的位长,u是C的最后一个块的位长,|| 表示位串的串联。
如何连接 A 块以填充从 v 到 128 位的零填充,因为我不知道 A 的整个块的长度。所以我只取 A 块并将其与 128 的数组进行异或位
void GHASH(uint8_t H[16], uint8_t len_A, uint8_t A_i[len_A], uint8_t len_C,
uint8_t C_i[len_C], uint8_t X_i[16]) {
uint8_t m;
uint8_t n;
uint8_t i;
uint8_t j;
uint8_t zeros[16] = {0};
if (i == m + n) {
for(j=16; j>=0; j--){
C_i[j] = C_i[j] ^ zeros[j]; //XOR with zero array to fill in 0 of length 128-u
tmp[j] = X_i[j] ^ C_i[j]; // X[m+n+1] XOR C[i] left shift by (128bit-u) and store into tmp
gmul(tmp, H, X_i); //Do Multiplication of tmp to H and store into X
}
}
我很确定我不正确。但我不知道该怎么做。